| Embryology
Rejects the Lie of Evolution
The event of birth is a proof of a supreme creation,
yet evolutionists try to make reference to it
in defence of their theory. The fact that, in
the creation of a new human being, every stage
develops according to a very delicate design,
is today an undisputed fact in the field of embryology.
In this case, how do evolutionists try to interpret
this fact of creation in reference to their theory?
 |
...My
Lord encompasses all things in His
knowledge so will you not pay heed?
(Qur'an, 6: 80) |
|
At the end of the 19th century, the evolutionist
biologist Ernst Haeckel proposed his thesis, "Ontogeny
Recapitulates Phylogeny". In this thesis, Haeckel
claimed that living embryos in the process of
their development repeat the evolutionary process
that their supposed ancestors went through. For
example, he proposed that a human embryo in its
mother's womb first displayed the characteristics
of a fish, then of a reptile before finally turning
into a human being.
| 
Evolutionist Haeckel
did not hesitate to produce fabricated
evidence. But as science advanced, it
was revealed that Haeckel's scenario was
purely imaginary.
|
Before long it was realized that this thesis
did not reflect the facts. The gills that supposedly
appeared in the first periods of a human embryo
were actually the human inner ear canal and the
parathyroid and thymus glands; the part of the
embryo resembling an egg yoke was actually the
sack responsible for the production of the baby's
blood; the part that was thought to be the tail
was identified as the human spine.
These are now facts well attested in the world
of science. Shortly after Haeckel proposed his
theory, evolutionists themselves acknowledged
that his claims were false. Two leading neo-Darwinists,
George Gaylord Simpson and W. Beck acknowledged
the invalidity of this theory:
Haeckel misstated the evolutionary principle
involved. It is now firmly established that ontogeny
does not repeat phylogeny.50
The validity of Haeckel's theory was also rejected
in scientific debate in the 1920's. After this,
in the 1950's, the theory was completely removed
from text books.51
Fabricated Drawings
In proposing his theory, Haeckel did not act
contrary to the tradition of evolutionist scientists;
he produced imaginary drawings to illustrate his
ideas. Even when embryology developed and it was
revealed that the drawings were fabricated, he
acknowledged that he had not followed a different
path from the rest of his colleagues:
After this compromising confession of 'forgery'
I should be obliged to consider myself condemned
and annihilated if I had not the consolation of
seeing side by side with me in the prisoner's
dock hundreds of fellow-culprits, among them many
of the most trusted observers and most esteemed
biologists. The great majority of all the diagrams
in the best biological textbooks, treatises and
journals would incur in the same degree the charge
of 'forgery,' for all of them are inexact, and
are more or less doctored, schematised and constructed.52
It can be understood from this confession that
Haeckel's attempts to use embryology as a proof
for evolution are completely without foundation
and amount to nothing more than sophistry. The
details we have given in the course of this book,
as general as they were, of the miracle of human
creation are an undeniable proof of the truth
of creation.
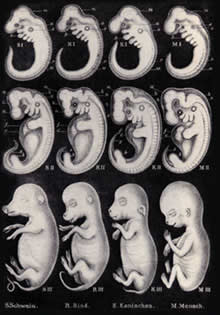
In Haeckel's fabricated drawings, the
embryos of various living things were
placed side by side in the attempt to
give the impression that there was a similarity
among them. In order to show the similarity
between the embryo of a human being and
that of a fish, Haeckel made a few additions
to some parts and removed other parts.
As in all other evolutionist falsifications,
the goal here was to provide false evidence
for evolution. But actual photographs
of these embryos clearly revealed Haeckel's
falsifications. These fabrications are
just one proof that the theory of evolution
is a deceit founded on falsehood. |
|
